US budget tax cuts show imbalance - loss for poor and gain for wealthy? Can it be corrected?
Summary
The proposed U.S. budget cuts to Medicaid, food assistance, and other programs are part of a plan by House Republicans to fund $4.5 trillion in tax cuts that would largely benefit the wealthy and corporations. The budget outlines $2 trillion in reductions to programs like Medicaid and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), with $880 billion in Medicaid cuts and $230 billion in SNAP reductions over the next decade.
These cuts are framed as necessary to reduce federal spending but would likely lead to millions losing healthcare coverage and increased food insecurity. Critics argue the tax cuts will still add trillions to the national debt, requiring a $4 trillion debt ceiling increase, while disproportionately benefiting billionaires and corporations. Proponents claim the cuts aim to address fraud and encourage workforce participation, though analysts warn of severe impacts on low-income Americans.
Affect of Budget cuts
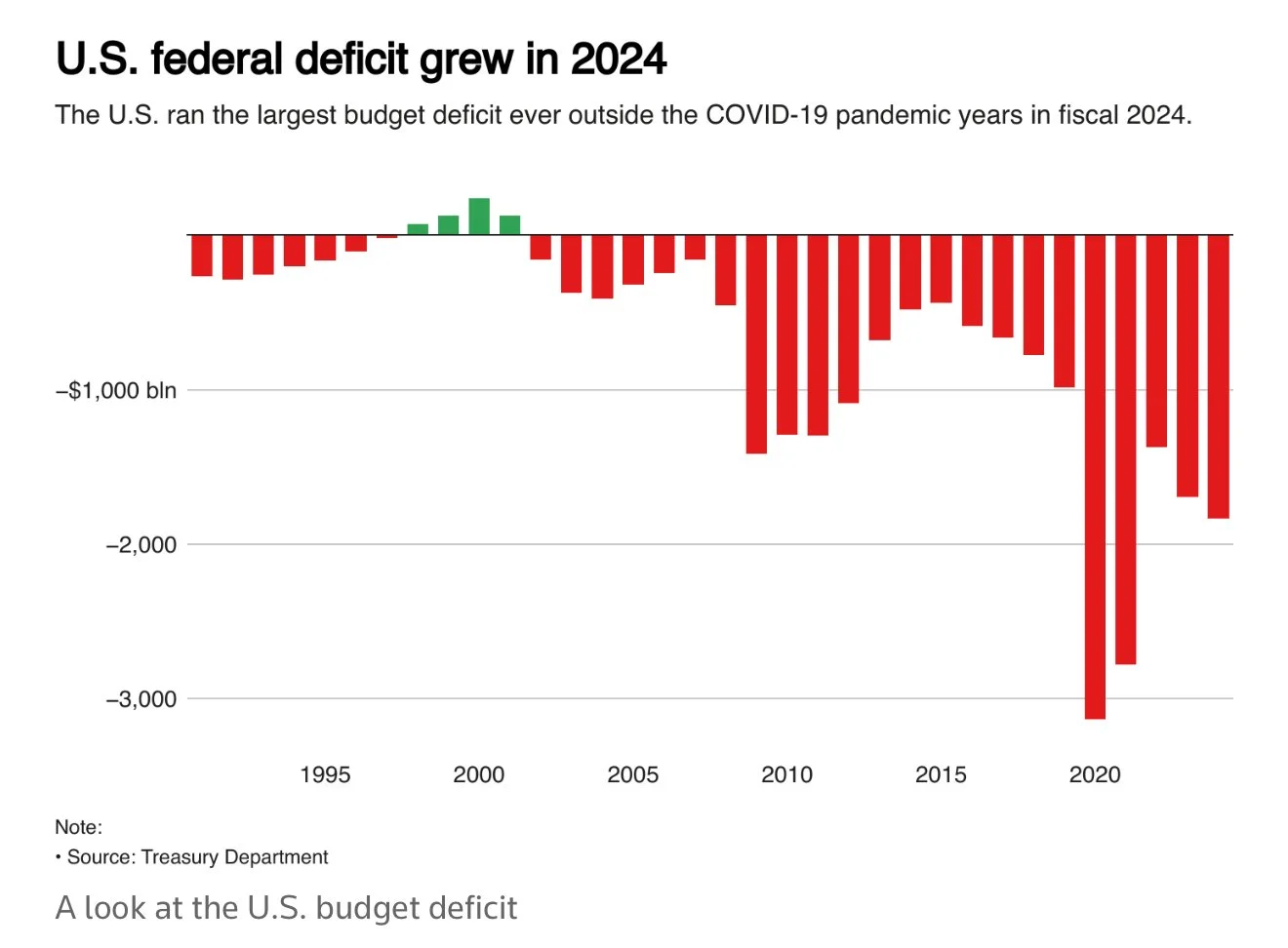
The proposed budget cuts to Medicaid, food assistance, and other programs could have mixed effects on the national debt.
While these cuts aim to reduce federal spending, the simultaneous $4.5 trillion in tax cuts for corporations and the wealthy would likely increase deficits, as tax cuts have historically been a major driver of debt growth, adding $10 trillion since 2001.
Spending cuts alone may stabilize debt in the short term but could slow economic growth by reducing consumer demand and increasing financial strain on low-income households.
Furthermore, high debt levels are already driving up interest rates, which increases borrowing costs and crowds out private investment.
Affect on Medicaid cut on low income families
The proposed Medicaid cuts would severely impact low-income families by reducing access to healthcare services, increasing financial strain, and exacerbating health disparities.
Loss of Coverage: Millions could lose Medicaid coverage, especially in states reversing Medicaid expansion. This includes vulnerable groups like children, seniors, and individuals with disabilities.
Reduced Services: Cuts may lead to the elimination of essential benefits (e.g., dental, vision) and stricter eligibility requirements, leaving families without critical care.
Financial Burden: Families could face higher out-of-pocket costs for medical care, risking medical debt and economic insecurity.
Impact on Children: Nearly half of U.S. children rely on Medicaid or CHIP. Cuts would reduce access to preventive care, developmental screenings, and treatment for complex conditions.
Healthcare Access Crisis
Lower provider reimbursements could result in fewer doctors accepting Medicaid, longer wait times, and closures of safety-net hospitals, particularly in rural areas.
Overall, these cuts would disproportionately harm low-income families while straining state budgets and healthcare systems.
Budget cuts affect the national debt
The proposed budget cuts to Medicaid, food assistance, and other programs may have limited impact on reducing the national debt when paired with $4.5 trillion in tax cuts for corporations and the wealthy. While spending reductions could marginally lower deficits, the tax cuts are likely to significantly increase the debt, as similar policies have added $10 trillion to the debt since 2001.
Additionally, high debt levels already drive up interest rates, slowing economic growth and increasing borrowing costs. Experts suggest that a balanced approach—combining targeted spending cuts, tax increases, and lower interest rates—would be more effective in stabilizing debt without exacerbating economic inequality or harming vulnerable populations.
Potential risks of not addressing the national debt
Failing to address the national debt poses significant risks across economic, fiscal, and geopolitical domains:
Higher Interest Costs: Rising debt leads to growing interest payments, which could exceed $12.9 trillion over the next decade, crowding out investments in critical areas like education, infrastructure, and healthcare.
Slower Economic Growth: High debt levels increase borrowing costs, reduce private investment, and slow productivity growth, ultimately lowering future living standards.
Reduced Crisis Response Flexibility: A large debt burden limits the government’s ability to respond to emergencies like recessions or pandemics, leaving the economy more vulnerable.
Geopolitical Risks: Dependence on foreign creditors weakens U.S. leverage in global affairs and increases vulnerability to external pressures.
Generational Inequity: Rising debt shifts financial burdens onto future generations, reducing their economic opportunities and fiscal flexibility.
Risk of Fiscal Crisis: Persistent deficits could undermine investor confidence, leading to higher interest rates or a “debt spiral,” potentially triggering a financial crisis.
National debt affect future generations' economic opportunities
The national debt significantly affects future generations’ economic opportunities by reducing resources available for investments that drive growth and prosperity. Key impacts include:
Crowded-Out Investments: Rising interest costs divert funds from critical areas like education, infrastructure, and research, which are essential for economic mobility and productivity.
Slower Economic Growth: High debt levels reduce private investment by increasing competition for capital, leading to lower wages, fewer jobs, and diminished innovation.
Higher Tax Burdens: Future generations may face increased taxes to service the debt, limiting their disposable income and financial flexibility.
Reduced Fiscal Flexibility: A large debt limits the government’s ability to respond to crises or invest in future priorities, leaving younger generations with fewer tools to address emerging challenges.
Weakened Economic Stability: Persistent debt increases risks of inflation, higher borrowing costs, and potential fiscal crises, which could destabilize the economy for future workers and families.
Conclusion
Without balanced reforms, such as combining spending cuts with revenue increases or lower interest rates, the national debt is likely to continue rising.
Addressing national debt risks requires balancing spending cuts and revenue increases to stabilize debt growth while maintaining economic vitality.
These effects create long-term disadvantages, making it harder for future generations to achieve economic security and prosperity.
FAF additional review
To cut the FY2025 budget without implementing $4.5 trillion in tax cuts for the wealthy and corporations, policymakers could focus on the following strategies:
Targeted Spending Reductions
Focus on reducing unnecessary discretionary spending, such as subsidies for industries or programs with limited public benefit.
Reform defense spending by eliminating waste and prioritizing efficiency without compromising national security.
Preserve Revenue Stream
Avoid extending tax cuts from the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), which disproportionately benefit high-income earners and corporations, as they do not pay for themselves or spur significant economic growth.
Close Tax Loopholes:
Eliminate tax breaks like carried interest deductions and excessive corporate subsidies, which could save billions.
Strengthen Progressive Taxation:
Increase taxes on the wealthiest individuals and corporations to ensure fair contributions while maintaining middle-class tax relief.
Invest in Growth:
Redirect funds toward infrastructure, education, and healthcare to stimulate long-term economic growth, which can reduce debt-to-GDP ratios over time.
Address Mandatory Spending:
Reform entitlement programs like Medicare and Social Security to ensure sustainability while protecting low-income beneficiaries.
Cut aid for all nations and drop the idea of taking over Gaza and Greenland.
Where will money come from?
Why is the government not focused on revenue generating areas I.e sell Defence equipment and services.
By focusing on these measures, the budget could achieve fiscal responsibility without exacerbating inequality or increasing the national debt through unfunded tax cuts.